Clean System Volume Information Windows 10
One of the servers (running Windows Server 2012 R2) has run out of free disk space on a system drive (C:). I checked and cleaned all resource-consuming locations (, TEMP folders, user profiles, etc.), but it didn’t give a noticeable effect. There was still not enough disk space. At last, I have found that a large part of a system disk has been occupied by System Volume Information folder. In this article I will try to tell you how the System Volume Information folder is used on Windows systems, what is stored in it, and how to clean it up.
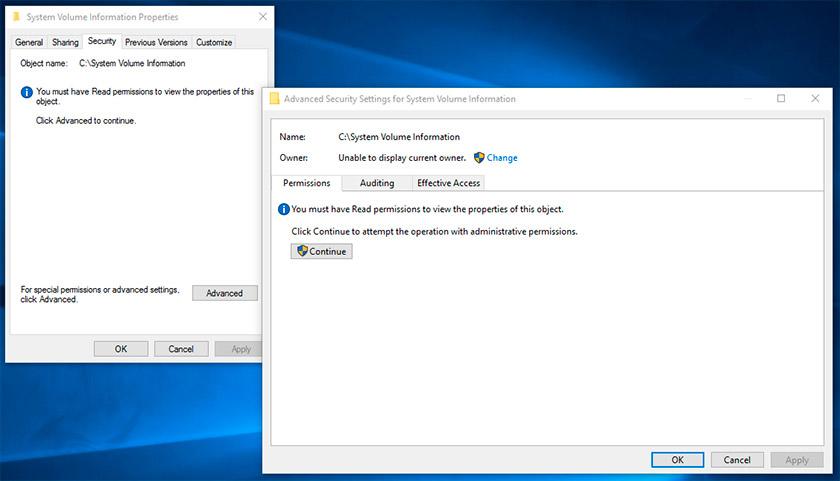
Contents:.How to Gain Access to the System Volume Information Folder?The System Volume Information folder is located at the root of each disk (be it a local HDD / SSD, or removable USB flash drive). It stores system data related to system recovery service, indexing, File History feature, etc.By default, the System Volume Information folder is hidden and only the SYSTEM has access to it. Even the administrator cannot open it and view the contents of the folder. If you try to open the System Volume Information folder in Explorer, under any user (even an administrator), you will receive an access denied error. To view the contents of the folder, you have to assign yourself as the directory owner and grant your account the NTFS permissions to access it (this can be done through the Security tab in the folder properties). But you can grant your account (for example, username) permissions to access the folder much faster with the command:icacls 'C:System Volume Information' /grant username:F /tCheck in the folder properties on the Security tab that your account has full access permissions to the folder.To restrict access to the System Volume Information folder, run:icacls 'C:System Volume Information' /remove username /t What is System Volume Information Folder Used For?What is stored in System Volume Information folder?
I found information about the following services, which store their files in this folder (the list is not exhaustive). When you run the wbadmin delete systemstatebackup command in Windows 10, an error appears: “ The DELETE BACKUP command is not supported in this version of Windows“. The fact is that in client systems (Windows 10/ 8.1/ 7), management of recovery points and limits is possible only from the GUI.
Open the System properties and click on the System Protection tab.By pressing Configure, we proceed to the settings of quotas for restore point storage. You can delete the existing restore points here.Select the system drive and click the Configure button. The quota configuration dialog box for storing system restore points will open.
How To Hide System Volume Information
You can reduce the size of the disk for storing shadow copies.